Y=x^tan x derivative 188470-Find the derivative of y=x tan x
All derivatives of circular trigonometric functions can be found from those of sin ( x) and cos ( x) by means of the quotient rule applied to functions such as tan ( x) = sin ( x )/cos ( x ) Knowing these derivatives, the derivatives of the inverse trigonometric functions areThe derivative of arctan x is 1/(1x^2) We can prove this either by using the first principle or by using the chain rule Learn more about the derivativeAnswer (1 of 6) y = (tan^1 x) (tan^1 1/x) It can be easily shown that d/dx (tan^1 x) = 1/(1x^2), So, dy/dx = 1/( 1 x^2) 1/(11/x^2) * d/dx (1/x) ( applying
Derivative Of Tangent X Sec X Tan X Longer Free Tutorial Get Education Bee
Find the derivative of y=x tan x
Find the derivative of y=x tan x-∴ The derivative of tan (sin x) is sec 2 (sin x) cos x Download Solution PDF Share on Whatsapp Ace your Mathematics and Differential Calculus preparations for Evaluation of derivatives with us and master Trigonometric Function for your exams Learn today!The first way of finding the derivative of illustrates why the graph of is the same as the graph of but shifted vertically by units It is easy to see that this argument can be extended for the gra Continue Reading There are at least two ways 1) Write as ,



Derivative Of Tan X
Derivative of tan inverse x Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for studentsNote that the function defined by y = x x is neither a power function of the form x k nor an exponential function of the form b x and the formulas of Differentiation of these functions cannot be used We need to find another method to find the first derivative of the above function If y = x x and x > 0 then ln y = ln (x x) Use properties of logarithmic functions to expand the right side of Now, there are four requirements to take the derivative of tan (x) Use the quotient rule for derivatives Take the derivative of sin (x) Take the
Derivative of y=tan x 1/ sec x We have a derivative of y equals tan x minus one upon sec x So, y dash can be equal to the tangent of an x minus one prime secant of x minus tan x minus one time the secant of x prime Next, we get the derivative of the tangent, which is secant squared x and times secant of x,Find the Derivative d/dx y=cos(x)tan(x) Differentiate using the Product Rule which states that is where and The derivative of with respect to is The derivative of with respect to is Simplify the expression Tap for more steps Move to the left of Rewrite as Reorder terms This answer is not useful Show activity on this post HINT, using the chain rule and the quotient rule d arctan ( f ( x)) d x = d f ( x) d x 1 f ( x) 2 = f ′ ( x) 1 f ( x) 2 f ′ ( x) = d d x ( 2 y ( x) y ( x) − v ( x)) = 2 ⋅ ( y ( x) − v ( x)) ⋅ d d x ( y ( x)) − y
Answer (1 of 9) \dfrac{\mathrm d}{\mathrm dx} \left(\dfrac{x}{\tan\,x}\right) =\dfrac{\tan\,x x \sec^2\,x}{\tan^2\,x} =\tan\,x \cot^2\,x x \sec^2\,x\cot^2\,xAre solved by group of students and teacher of Mathematics, which is also the largest student community of MathematicsTo find the derivative of y = tan x, we will use the quotient rule Answer The derivative of y = tan(x) is sec 2 (x) Following is the way to get the derivative of y = tan x Explanation Given, y = tan x Let u = sin x and v = cos x On applying quotient rule on y = sin x / cos x, we get,




Misc 17 Solve Tan 1 X Y Tan 1 X Y X Y Mcq Class 12



Derivative Of Tan X Wyzant Lessons
The functions f and g in the chain rule are here f (x) = sin (x) and g ( x) = tan x 2 You have y = f ( g ( x)) The chain rule says y ′ = f ′ ( g ( x)) ⋅ g ′ ( x) You can now go ahead and derive f and g and put them into the formula – Friedrich Philipp at 517Since the derivative of tan inverse x is 1/(1 x 2), we will differentiate tan1 x with respect to another function, that is, cot1 x For this, we will assume cot1 x to be equal to some variable, say z, and then find the derivative of tan inverse x wrt cot1 x Assume y = tan1 x ⇒ tan y = x Differentiating tan y = x wrt x, we get sec 2 y (dy/dx) = 1 Calculus Differentiating Trigonometric Functions Derivative Rules for y=cos (x) and y=tan (x) 1 Answer Ratnaker Mehta dy dx = − x2 1 x2 Explanation x = tan(x y) Diffing, both sides wrt y, and keeping in mind the Chain Rule, dx dy = d dy tan(x y) = (sec2(x y)) d dy (x y) = sec2(x y) ⋅ ( dx dy 1)




If Y Secx Tanxsecx Tanx Show That Dydx Sec X Tan X Sec X




What Is The Derivative Of Y Tan X Socratic
How do you find the derivative of y = tan(x) using first principle? tex=2x\sec^{2}x\tan x2\sec^{2}x/tex What you did was increase the power rather than decreasing it In general, the derivative of secant raised to a power isY = sec(tan x) , find the derivative



3




Derivative Of Tan X Formula Proof Examples Differentiation Of Tan X
Derivative of Tan x Proof by Chain Rule We will prove the differentiation of tan x formul m What is the derivative of y = tan(x y)?Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Find the derivative of x cosxtanx Solve Study Textbooks Guides Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Applied Mathematics >> Differentiation >> Rules of differentiation Find the derivative of tan x x cos x




If Y Tan 1x 2 Show That X 2 1 2y2 2x X 2 1 2



Find The Derivative Of Y Sin X Cos X Tan X Youtube
Answer (1 of 4) y = tan(xy) y' = sec²(xy) (1 y') y' y' sec²(xy) = sec²(xy) y' = sec²(xy) / 1 sec²(xy) = 1 / cos²(xy)1 = 1 / sin²Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for studentsThe derivative of tan ( x) tan ( x) with respect to x x is sec 2 ( x) sec 2 ( x) Multiply sec 2 ( x) sec 2 ( x) by sec 2 ( x) sec 2 ( x) by adding the exponents Tap for more steps Use the power rule a m a n = a m n a m a n = a m n to combine exponents Add 2 2 and 2 2



What Is The 2nd Derivative Of Y Tanx Socratic




Ex 5 3 4 Find Dy Dx In Xy Y2 Tan X Y Chapter 5
This is a type of problem involving logarithmic differentiation Whenever you're trying to differentiate a variable raised to some power also involving that variable, it's a good hint that logarithmic differentiation will help you out 1) y = xtanx The first step is to take the natural log of both sides 2) lny = lnxtanxYou need to use the chain rule to find the derivative of the function First, find the derivative of the outer function and then do the derivative of inner function mathy'=sec^2 (xy)frac {d}/ {dx} (xy) /math math=sec^2 (xy) /math 17K views View upvotes Answer requested by Amrit Anand Kishore Prabhu S Use logarithmic differentiation let #y=x^{tan(x)}# so that #ln(y)=ln(x^{tan(x)})=tan(x)ln(x)# Now differentiate both sides with respect to #x#, keeping in mind that #y# is a function of #x# and using the Chain Rule and Product Rule #1/y * dy/dx=sec^{2}(x)ln(x)tan(x)/x# Hence, #dy/dx=y * (ln(x)sec^{2}(x)tan(x)/x)#




Differentiate Xtanx Secx Tanx




Lecture 5 5 The Derivative Of Y Tan X Youtube
You to the X squared White time, minus seeds of the wine and on the other side of the equation will have one minus two x y me to the X Square in a way, and we can divide both sides by the expression to get one minus two x y e to the X squared one all over X square in times E to the X squared y minus, even the way All right, 9 #1 I am working on a homework problem which asks for the derivative of y = (tan x)^ ln x My strategy is to take the natural log of both sides which gives me ln y = ln (x) *ln (tan x) , after bringing down the ln (x) From here I am using implicit differentiation and the "product rule" and then plugging the original (tan xClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Find the derivative of tan x using first principle of derivatives Solve Study Textbooks Guides Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Maths >> Limits and Derivatives >> Derivative of Trigonometric Functions




Differentiate The Following With Respect Of X X Secx X Tanx



What Is The Derivative Of Sinx Tanx Quora
India's #1 Learning PlatformY 2 ( x − 1) y = t a n ( x) Divide x1, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac {x1} {2} Then add the square of \frac {x1} {2} to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect square Divide x − 1, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get 2 x − 1The derivative of tanx The derivative of sec x tan x Suppose we have y=f(x)⋅g(x) Then, using Product Rule, y'=f(x)⋅g'(x)f'(x)⋅g(x) In simple language, keep the first term as it is and differentiate the second term, then differentiate the first term and keep the second term as it is or viceversa derivative of secx tanx Derivative of tanx^1



Solved Find The Equation Of The Tangent Line To The Curve At Chegg Com




Differentiate Xtanx Secx Tanx
Derivative of tan (xy) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving processFind the derivative of `y=Tan^(1)(tanh""(x)/(2))` Updated On This browser does not support the video element Get Answer to any question, just click a photo and upload the photo and get the answer completely free, UPLOAD PHOTO AND GET THE ANSWER NOW! The Questions and Answers of Find the derivative of Tan (x) = Tan (y)a)b)c)d)Correct answer is option 'A' Can you explain this answer?
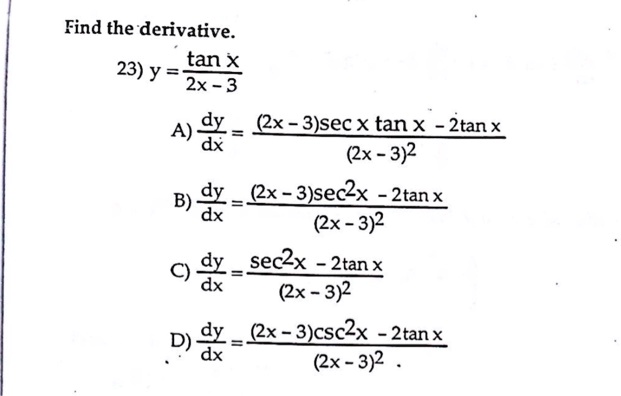



Solved Find The Derivative 23 Y Tan X 2x 3 A Dx 2x 3 Sec X Tan X 2tan X 2x 3 2 B Dx 2x 3 Sec2x 2tan X 2x
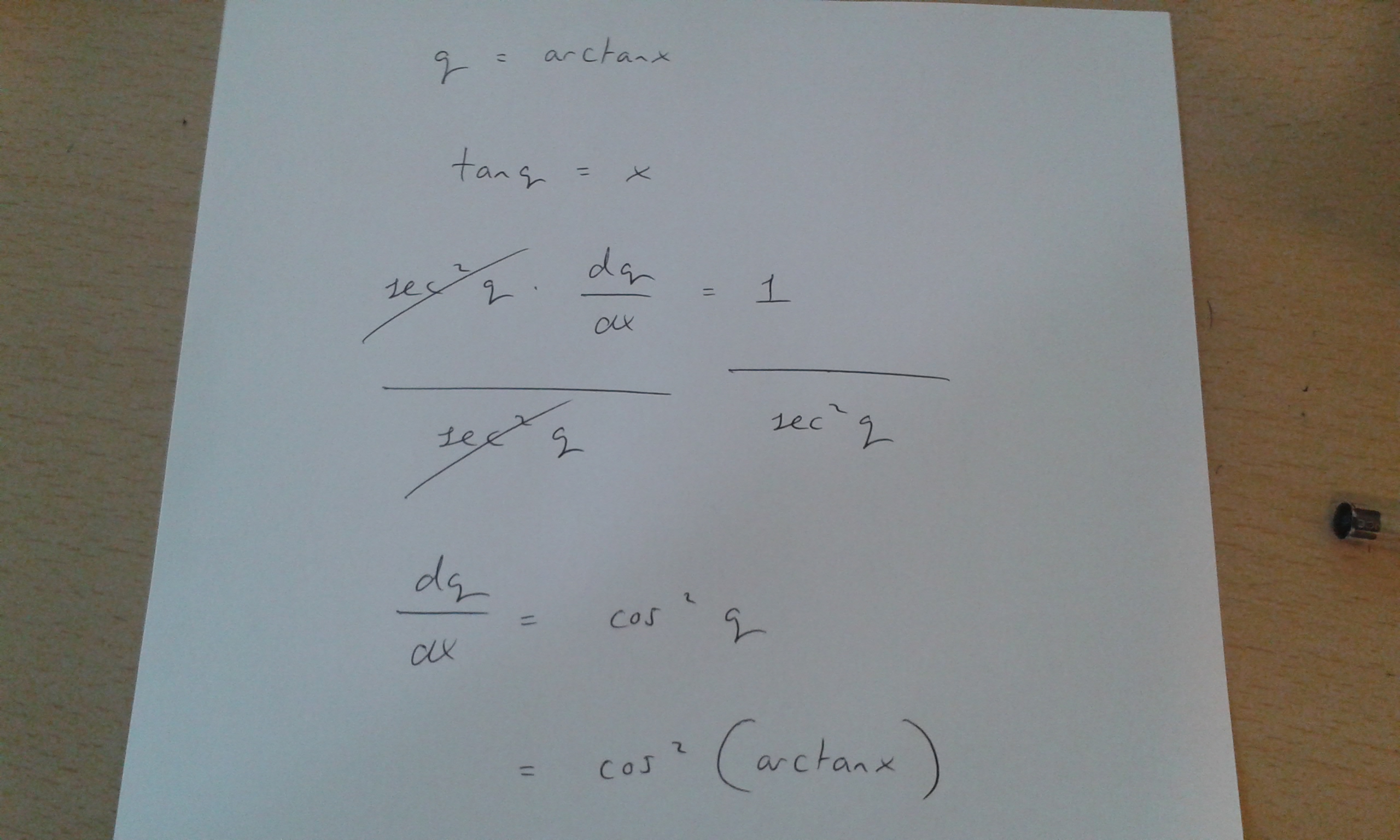



How Do You Find The Derivative Y Sqrt Tan 1 X Socratic
Calculus Differentiating Trigonometric Functions Derivative Rules for y=cos (x) and y=tan (x) 1 Answer Ratnaker Mehta ∴ dy dx = − 1 y2 y2, or, = − csc2(x y) Explanation y = tan(x y) ⇒ tan−1y = x y ⇒ tan−1y −y = x Diffing wrt y, we have, 1 1 y2 −1 = dx dy ∴ 1 − 1 − y2 1 y2 = dx dyExpert Answers Tushar Chandra Certified Educator Share Cite It is given that x = tan y To determine the derivative , use implicit differentiation 1 = Misc 29 Find the derivative of the following functions (it is to be understood that a, b, c, d, p, q, r and s are fixed nonzero constants and m and n are integers
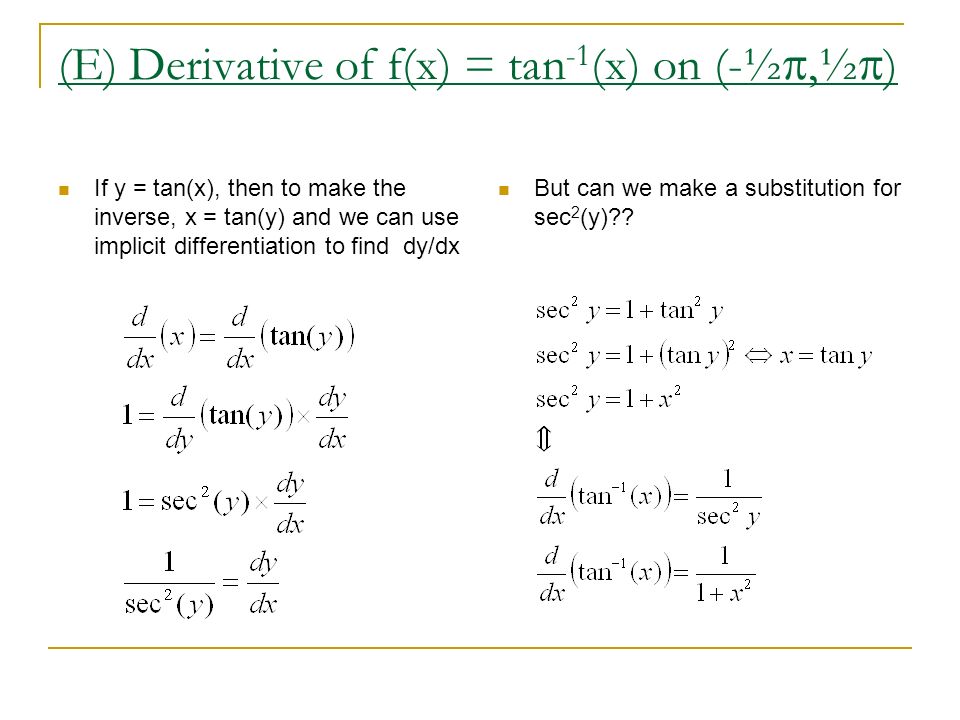



B1 6 Derivatives Of Inverse Trig Functions Ppt Download



If Y Log 1 Tan X 1 Tan X Prove That Dy Dx Sec 2x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Y = tan^3(x) , find the derivativeCalculus Find dy/dx x=tan (y) x = tan (y) x = tan ( y) Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (x) = d dx (tan(y)) d d x ( x) = d d x ( tan ( y)) Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that d dx xn d d x x n is nxn−1 n x n 1 where n = 1 n = 1 1 1We can prove the derivative of cot x formula by chain ruleFor this, let us recall that cot and tan are reciprocals of each other So we can write y = cot x as y = 1 / (tan x) = (tan x)1Since we have power here, we can apply the power rule here




Misc 29 Find Derivative X Sec X X Tan X Miscellaneous




Y X Tanx Sec X Tanx Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com
Free derivative calculator differentiate functions with all the steps Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graphSunita today special equation in which we have to find the derivative of tan x Y equal to y cube with it so we can start with the given equation into the equation is standard 1 Y equal to buy now button to the difference between of white cube into the formula of X rays with safe power should increase and decrease the differences of this line is differentiation of tan Square X Y now we Misc 25 Find the derivative of the following functions (it is to be understood that a, b, c, d, p, q, r and s are fixed nonzero constants and m and n are integers




Answered Find The Derivative Y 3 Tan X Bartleby




Use Quotient Rule To Find Derivative Of Y Tanx Youtube
//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=KMPrzZ4NTtc Next https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=pD8vBTwDC0o&list=PLJma5dJyAqpm1CGBaNMTmN0QGYbJk7D9&index=14 #GCSE #SAT #EQThe derivative of any function y = f(x) of a variable x is a measure of the rate at which the value y changes with respect to the change of x Answer The derivative of y = tan 2 x is dy/dx = 2 sec 2 x tan x Let us proceed for this problem step by step Explanation We can proceed by using chain rule It states that for any function, y = f(g(x))




Differentiate Xtanx Secx Tanx




Differentiate Y X 2 Sin X Tan X Product Rule Youtube




Differentiate Log X Tan X W R T Sin M Cos X Snapsolve




Solved The Derivative Of A Function Gives The Slope Of The Chegg Com




How To Take The Derivative Of Tan X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Differentiate The Following Functions W R T X E X Tan X Youtube




Find Derivative Dy Dx Of X Tan Y Implicit Differentiation Youtube




Find The Derivative Of Y X Tan X
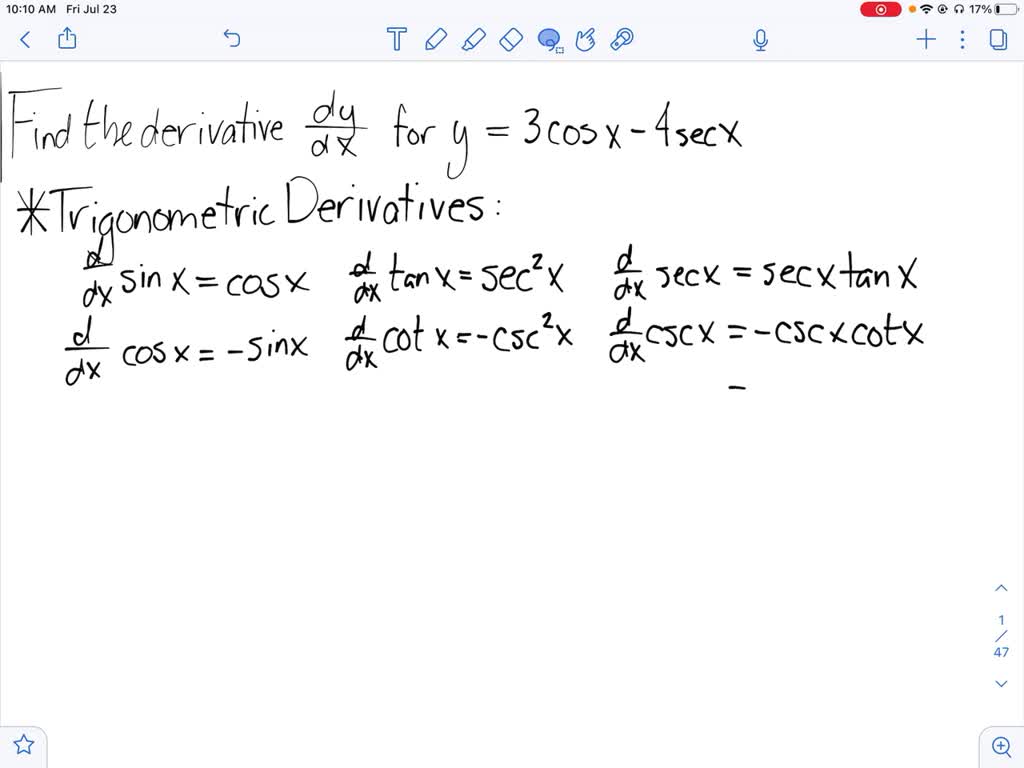



Solved Differentiate The Function Y 3 Cos X 4 Sec X



Differentiate Wrt X Y X Tan X Secx Tanx Mathematics Topperlearning Com




Find The Derivative Of X 2 Tan X Using The First Principle Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com




If Y Tan X Logsin X Then Y At X Pi4 Is



Find The Derivative Of Following Functions W R T X I Tan 1 A X 1 Ax Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Example 38 Find D2y Dx2 If Y X3 Tan X Chapter 5




How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y Xtan X Y X Tan X Brainly Com
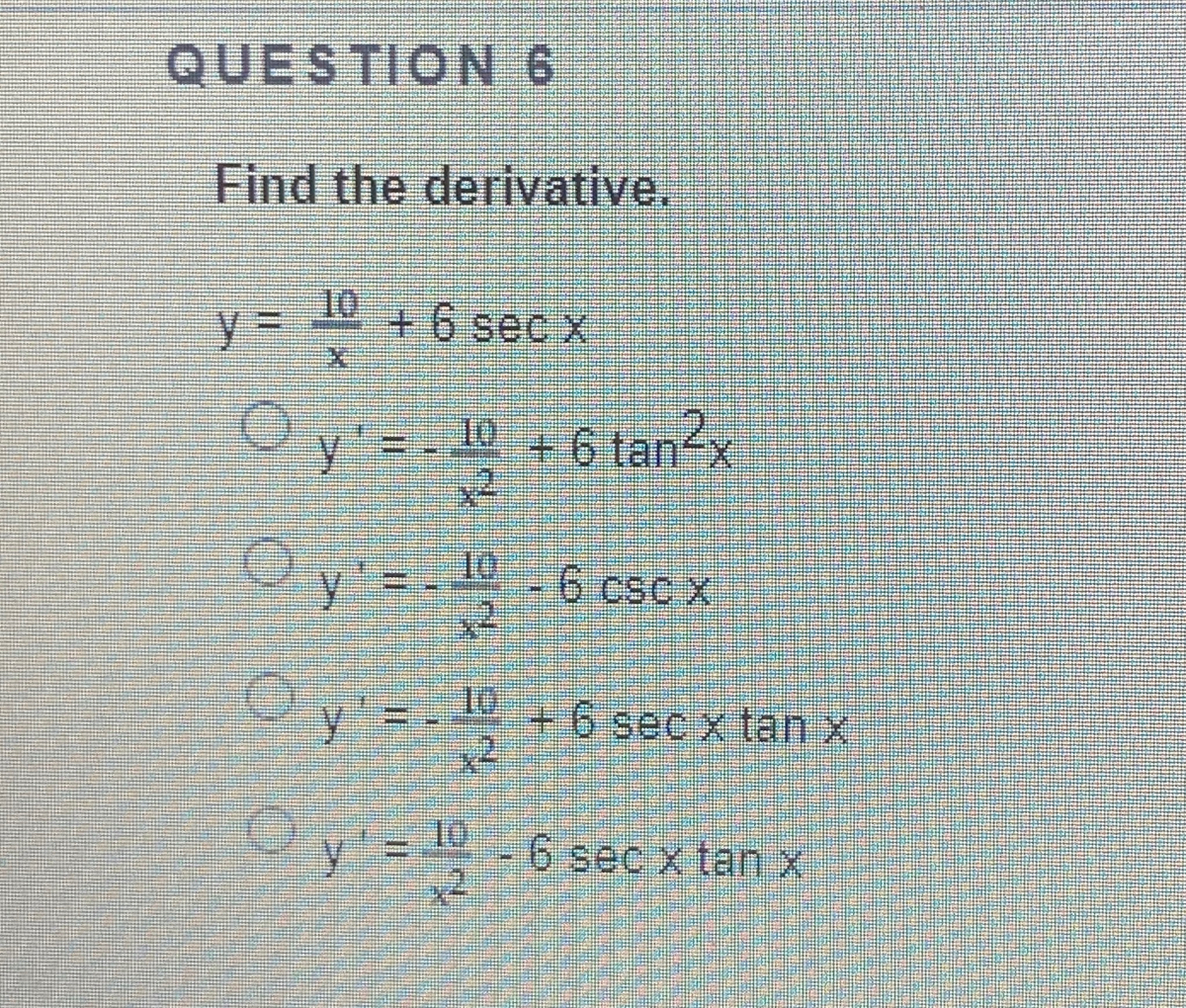



Answered Question 6 Find The Derivative 10 Y Bartleby
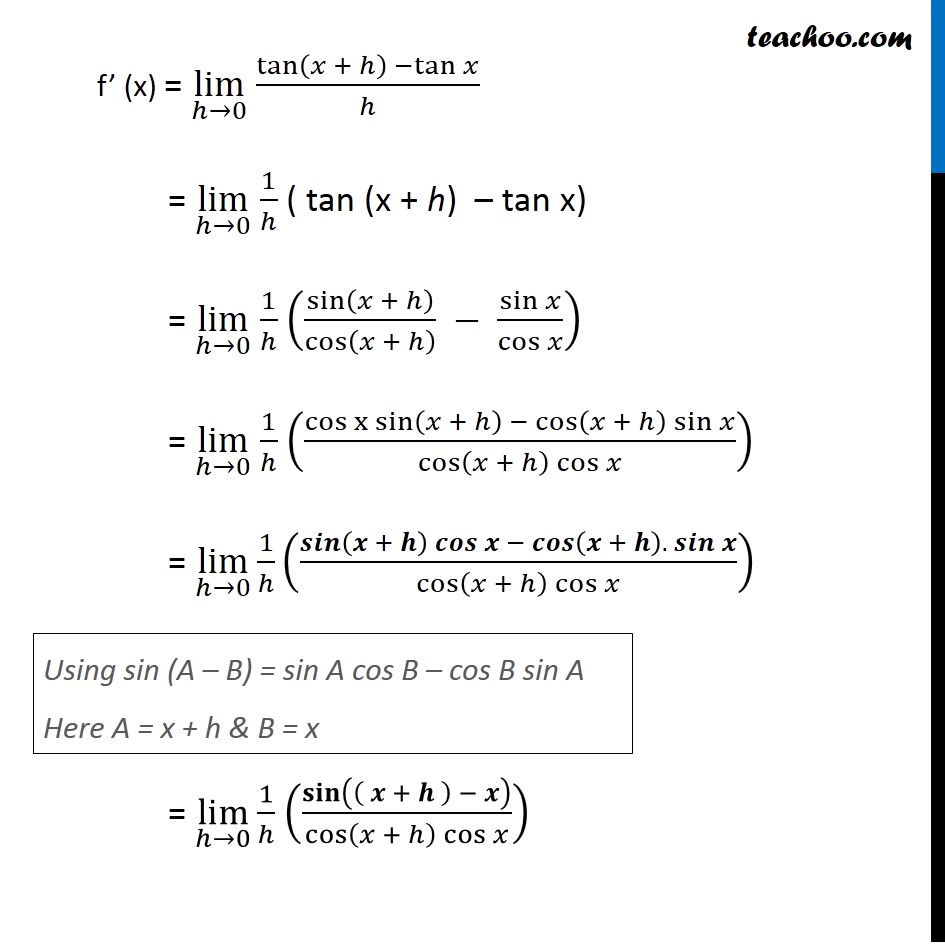



Prove That Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X By First Principle




Differentiate Each Of The Following W R T X Tan 3 X



Derivative Of Tan X




What Is The Derivative Of X Cosx Tanx Socratic




Solved What Is The Derivative Of The Function Y X Tan X Chegg Com




Solved Derive The Formula For The Derivative Of Y Tan X Chegg Com




Solved Find The Derivative 29 Y 8 10 Secx A Y 10 Chegg Com




Y Ln X Tan X Use Logarithmic Differentiation To Find Y Dy Dx Youtube




Example 27 Find Derivative Of F X Tan 1 X Class 12




Why Does Implicit Derivative Change After Division For Sec X Tan Y Sec X Tan Y Mathematics Stack Exchange




Misc 29 Find Derivative X Sec X X Tan X Miscellaneous




How Do You Differentiate Y Sin X 6 Tan X 2 X 2 2 2 Socratic



What Is The Second Derivative Of Tanx Secx Quora




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More



Differentiate The Following W R T Y X 5 Tan X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



The Derivative Of Tan X W R T G Sec X At X P 4 Where F 1 2 And G 2 4 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More




Packet 5 Derivative Shortcuts Ppt Download




Solved Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Tan X Y Chegg Com



Deriving The Derivative Of Inverse Tangent Or Y Arctan X Youtube




Differentiate X Tanx Tanx X With Respect To X



Derivative Of Tangent X Sec X Tan X Longer Free Tutorial Get Education Bee




Find Differentiation Of Sec 1tan X




Ex 5 7 8 Find Second Order Derivatives Of Tan 1 X Ex 5 7




Find The Derivative With Respect To X Tan X Y Tan X Y 1 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com
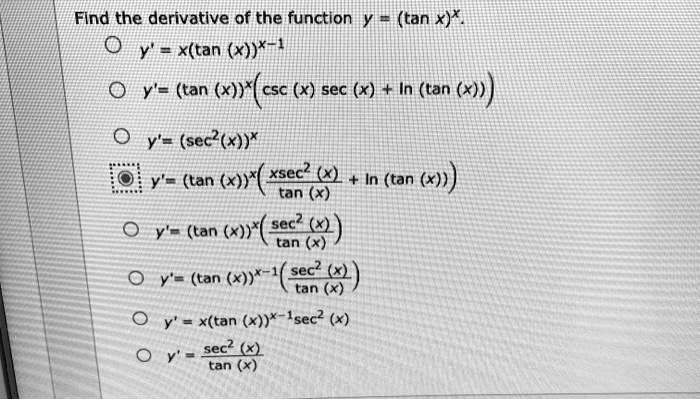



Solved Find The Derivative Of The Function Y X Tan X X 1 Tan X Y Tan X Csc X Sec X In Tan X Y Sec X Tan X Xsec




Derivative Of Tan Inverse X Formula What Is Derivative Of Arctan




Partial Derivative If U X 2 Tan 1 Y X Y 2 Tan 1 X Y Prove ә 2u әxәy X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Youtube




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More
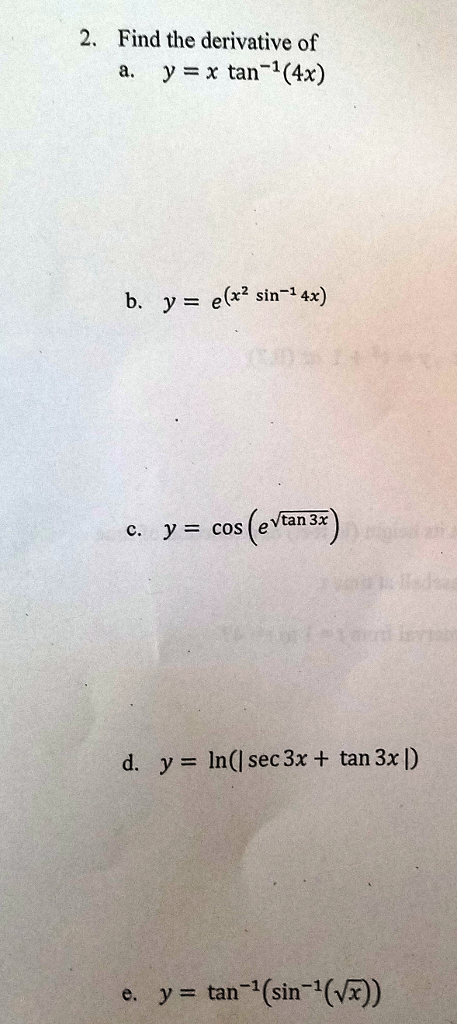



Solved 2 Find The Derivative Of Y X Tan 1 40 B Y E X2 Chegg Com



Derivatives Of Sin X Cos X Tan X Eˣ Ln X Video Khan Academy



Graph Of Y Tan X Video Trigonometry Khan Academy




Misc 25 Find Derivative X Cos X X Tan X Miscellaneous
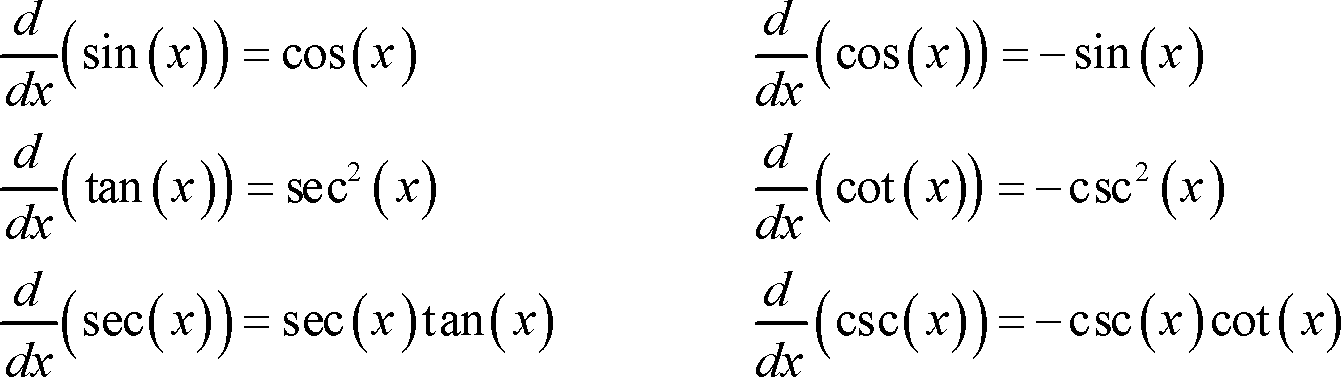



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y Tanx Cotx Socratic



How To Calculate The Differentiation Of Tanx Quora




Derivative Of Tan Inverse With Chain Rule Youtube




Answered Solve The Following 1 G X Bartleby




Calculus Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange




If Tan X Tan 2 X 1 Then The Value Of Tan 4 X 2 Tan 3 X Tan 2 X 2tan X 1 Is




Derivative Of Tan X Sec X Tan X More
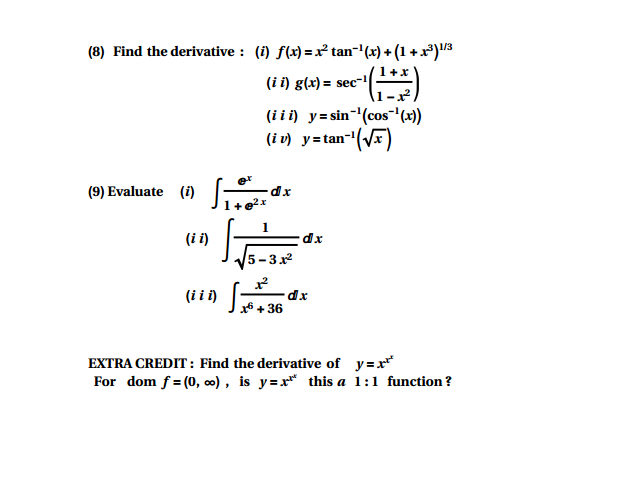



Solved Find The Derivative I F X X 2 Tan 1 X 1 Chegg Com




Solved Question 9 1 Point Differentiate Y Xsecx Using Chegg Com



1



What Is The Nth Derivative Of The Tan Inverse 1 X 1 X Quora




How To Take The Derivative Of Tan X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
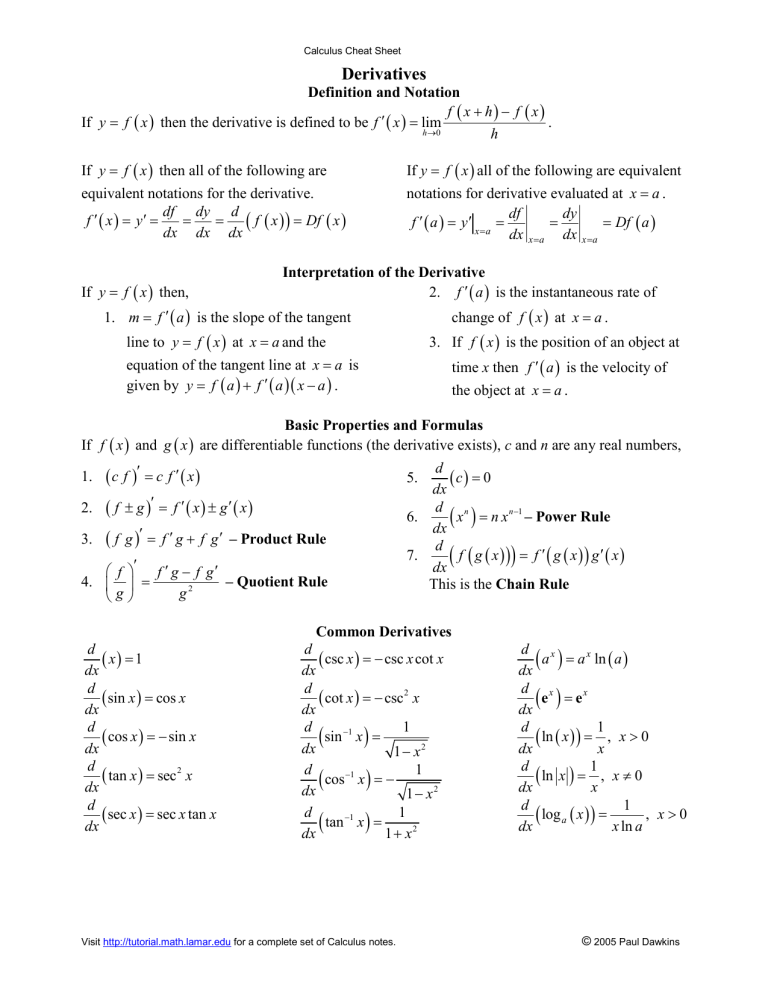



Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives 1



Solve The Following Differential Equation X Dy Dx Y X Tan Y X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




What Is The Equation Of The Tangent Line Of F X Xtanx Xcosx 1 X At X Pi 4 Socratic
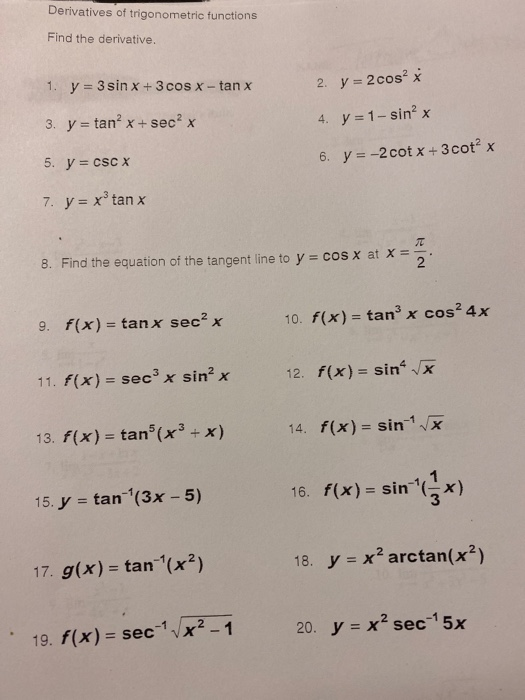



Solved Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions Find The Chegg Com




Derivative Of Sec X Formula Proof Of Differentiation Of Sec X By First Principle Examples



Find Dy Dx When Y X Cos X Sin X Tan X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
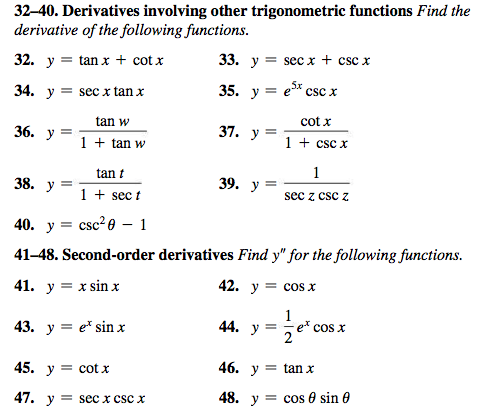



Solved 32 40 Derivatives Involving Other Trigonometric Chegg Com




Misc 28 Find Derivative X 1 Tan X Chapter 13 Class 11
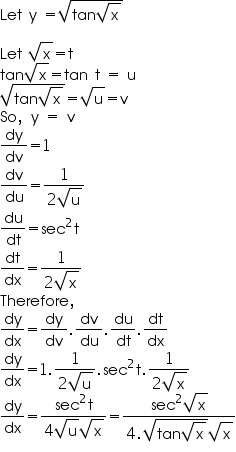



Find The Derivative Of Root Of Tan Of Root X Mathematics Topperlearning Com Y2z1m9aa




Derivative Of Y Tanx Youtube




Differentiate X 4tan X Maths Questions



1



If Y Log 1 Tan X 1 Tan X Prove That Dy Dx Sec 2x Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Prove That Derivative Of Tan X Is Sec 2 X By First Principle
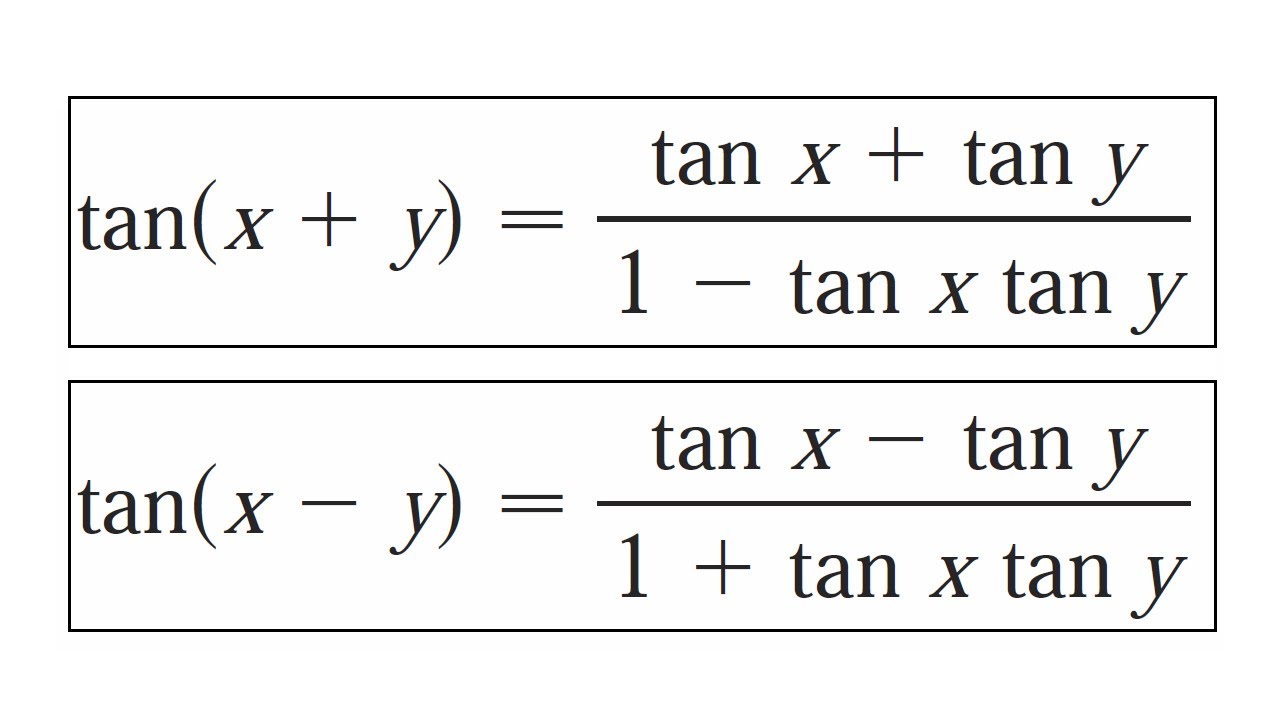



Trigonometric Identity Tan X Y Proof Youtube




What Is The Derivative Of Tanx X Socratic



3




Example 27 Find Derivative Of F X Tan 1 X Class 12



Find The Derivative Of F E Tan X W R T X At X 0 It Is Given That F 1 5 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



コメント
コメントを投稿